Over the past two decades, procurement has undergone a fundamental shift in many organizations: What was once a function focused on transaction processing and managing administrative tasks has become a driver of strategic value. This transformation was sparked by the realization that organizations could unlock significant benefits by taking a more analytical and holistic approach that uses data from markets, suppliers, and spending to inform sourcing strategies and business decisions.
As a result of this shift, leading organizations have moved beyond siloed management and isolated technology solutions to embrace end-to-end procurement models that deliver value through clear governance, streamlined processes, and enabling technology. Drawing on research and insights by Trey Robinson and John Francis (partners and supply chain co-leads for management consulting firm ScottMadden), this article explores the business drivers behind procurement’s evolution, introduces a tiered service delivery model designed to address common problems in the procure-to-pay process, and outlines practical steps to implement and sustain meaningful change.
Build a Foundation with End-to-End Governance
In the end-to-end P2P process, many downstream inefficiencies in Accounts Payable and Materials Management have a root cause in procurement and planning. Transforming procurement includes changing the way the process is governed. Francis explained that as part of procurement’s strategic shift, procurement groups “have started to understand their impacts on accounts payable (AP),” which has led both procurement and AP to move toward an end-to-end procure-to-pay (P2P) process.
There are at least three reasons why you should consider end-to-end governance as part of a broader procurement transformation:
- End-to-end processes such as P2P often cross functional boundaries, requiring cross-functional coordination beyond silos.
- Strong governance structures align procurement and accounts payable, clarify reporting relationships, and support strategic goals.
- Governance through a single end-to-end process owner drives a strong mandate for standardization—an important prerequisite for implementing technology and shared services.
Governing Procure-to-Pay As An End-to-End Process
Learn how centralized ownership and clear structures can drive strategic impact across your supply chain.

Identify and Address Challenges in P2P
P2P is an end-to-end process that comprises multiple procurement and finance processes. As organizations execute this process across functions and business areas, plenty of things can go wrong along the way. There are three broad symptoms that point to the need for P2P improvement:
- Unclear roles: Strategic roles are completing transactional tasks and at times, transactional roles are being asked to execute strategic work.
- Activity without achievement: Partners and vendors see procurement as busywork that gets in the way of what they really need to accomplish.
- Uncertain service access: Once procurement is centralized, people don’t know where to go for help. In some cases, they will reach out to someone they know when there may be more efficient ways to access service.
These challenges often stem from the design of the end-to-end process model or the structures that support the process.
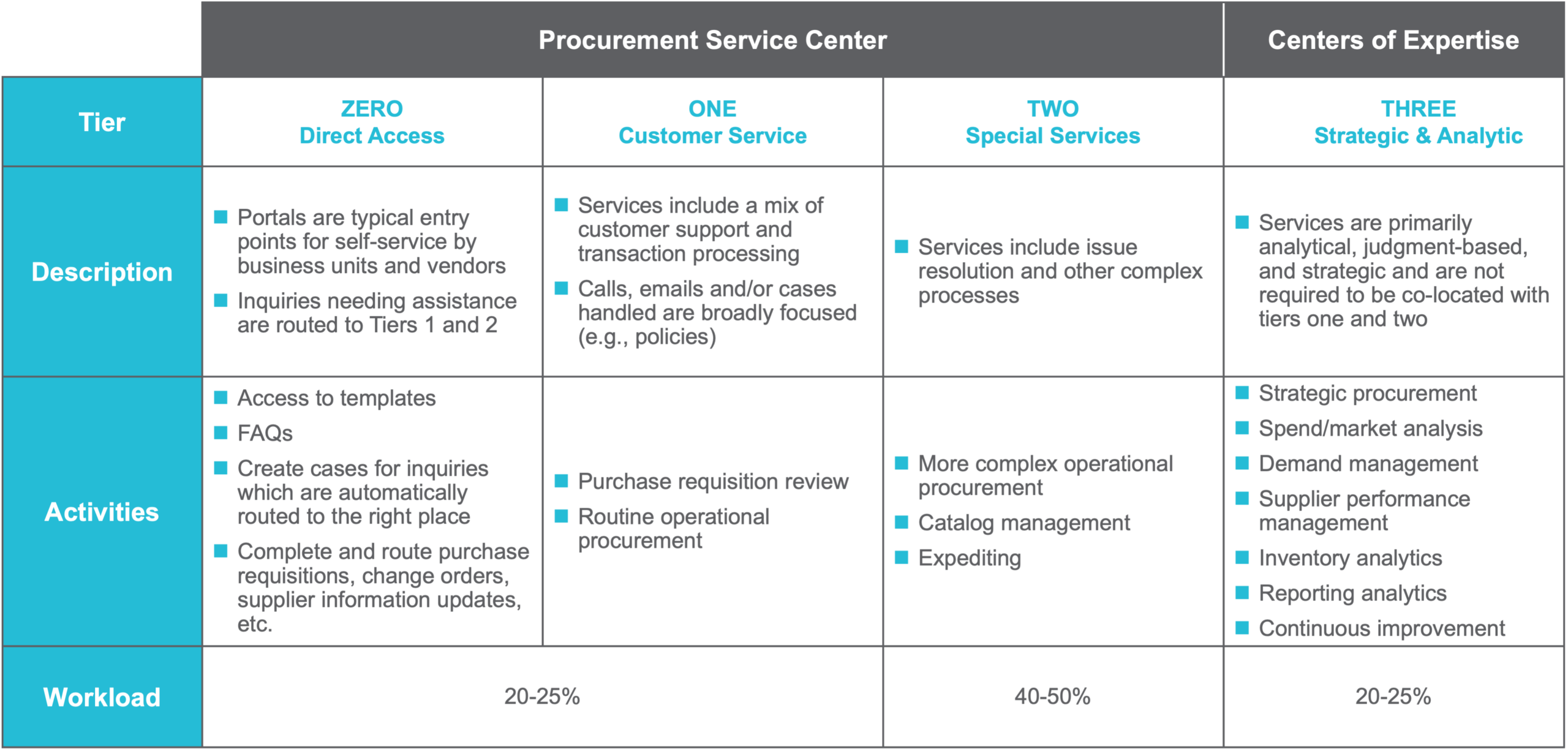
A tiered service delivery model like the one shown in Figure 1 can help you avoid common P2P challenges. For example, the model includes clearly scoped roles for different tiers, which will help you avoid confusion about who should be doing what or where customers should seek help for their issue. Customers with simple requests can leverage self-service tools and templates at tier 0 or escalate through tiers 1-3 depending on the complexity of their need.
How to Diagnose and Fix Problems with Your Procure-to-Pay Model
Learn more about how a tiered service delivery model can help you address some of the most common P2P challenges.

Enable Shared Services with Technology
Technology enables work at each tier of the shared services procurement delivery model. For example:
- Tier 0 (Direct Access) uses technology like self-service portals, chatbots, and automated assistants to handle routine questions and requests, minimizing the need for human intervention.
- In Tiers 1 and 2 (the procurement service center), organizations typically use case management systems, RPA, and ERP integrations to handle higher-volume, standardized requests and more complex problem resolution.
- Tier 3 (centers of expertise) use advanced analytics, predictive AI, and contract management tools to support strategic sourcing, supplier management, and continuous improvement. At this tier, technology augments human expertise, providing richer insights and enabling more informed decision-making.
Generative AI is poised to deliver dramatic efficiency gains across the procurement service delivery model. ScottMadden anticipates that the need for human effort at Tier 1 could decline by 50-80% over the next five years, with significant reductions in Tiers 2 and 3 as well.
How Technology Enables a Tiered Procure-to-Pay Service Delivery Model
Learn more about how leading organizations use emerging technologies to drive strategic value in procurement.

Transition to a New Model for Procurement
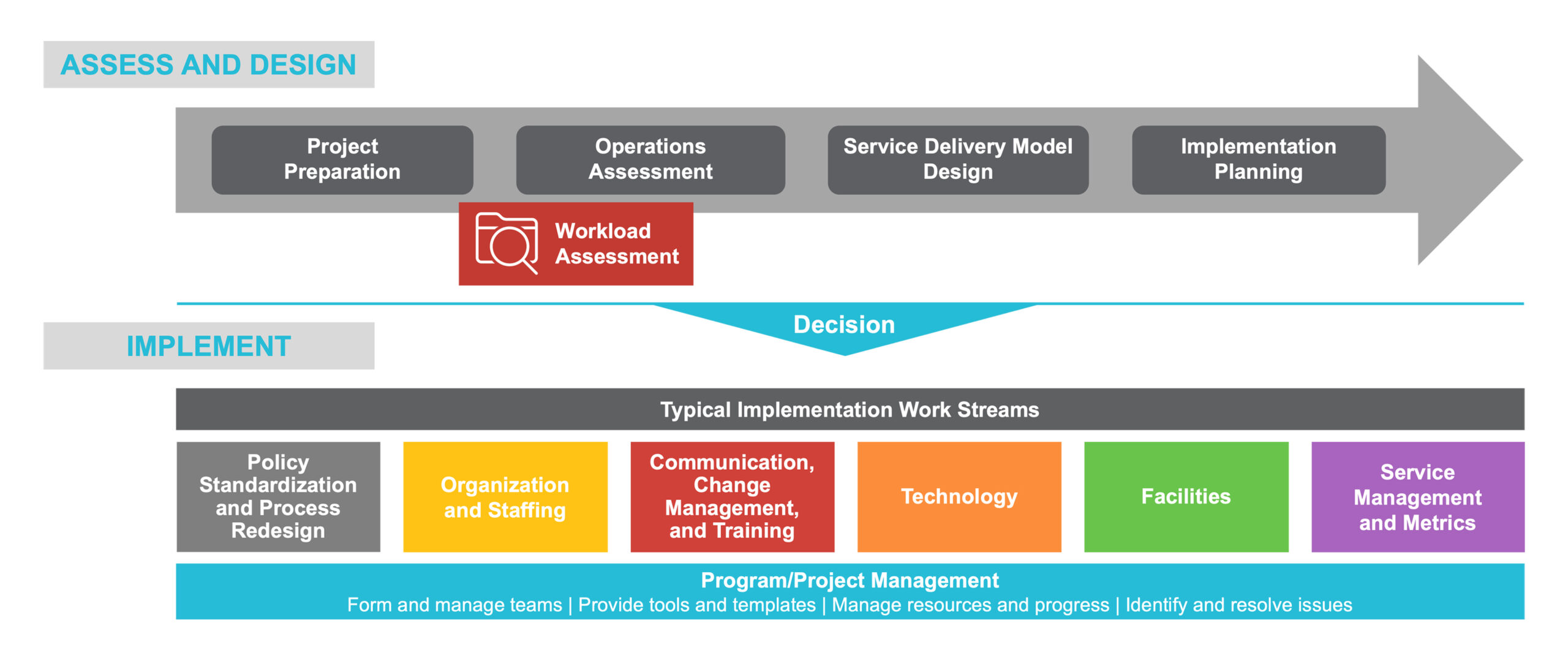
The journey to transform procurement into a more strategic services model typically includes five broad stages:
- Assessment of the current state process
- Design of an ideal future state process
- Implementation
- Stabilization
- Continuous Improvement
Organizations typically move through these transformation stages in two main phases:
- Assessment and design: A period of preparation, benchmarking, and development
- Implementation: Organizations select and configure technology, expand or establish shared service centers, train staff, and pilot changes before rolling the transformation out more broadly.
Figure 2 shows the typical approach at a high level.
How to Design and Implement a New Procurement Model
Learn more about the transformation journey, common transformation workstreams, and leading practices for implementation.

The Ongoing Journey to Procurement Excellence
Procurement transformation is an ongoing journey that requires vision, adaptability, and a willingness to rethink established ways of working. The steps, strategies, and tools outlined in this article come directly from successful procurement transformations across a wide range of organizations and industries. Following these approaches enables a smoother and more seamless transformation that delivers higher customer satisfaction and drives more value for the business.
About ScottMadden
ScottMadden has been a pioneer in corporate and shared services and has been helping supply chain organizations move beyond their conventional “order taker” role for over two decades. Through deep expertise and practical know-how, ScottMadden assists clients across the full range of supply chain processes and has the unique ability to create alignment between the supply chain function and its internal customers and stakeholders. ScottMadden has developed a supply chain maturity model to differentiate the phases that companies pass through on their journey to world class. Our solutions provide lasting improvements and allow our clients’ supply chain organizations to better serve their internal customers. Our clients span a variety of industries from energy to healthcare to higher education to retail. To learn more, visit https://www.scottmadden.com/topic/procure-to-pay/.
About APQC
APQC (American Productivity & Quality Center) is the world’s foremost authority in benchmarking, best practices, process and performance improvement, and knowledge management (KM). With more than 1,000 member organizations worldwide, APQC provides the information, data, and insights organizations need to support decision-making and develop internal skills. Learn more.
This content includes median values sourced from APQC’s Open Standards Benchmarking database. If you’re interested in having access to the 25th and 75th percentiles or additional metrics, including various peer group cuts, they are either available through a benchmark license or the Benchmarks on Demand tool depending on your organization’s membership type.
APQC’s Resource Library content leverages data from multiple sources. The Open Standards Benchmark repository is updated on a nightly cadence, whereas other data sources have differing schedules. To provide as much transparency as possible, APQC will always attempt to provide context for the data included in our content and leverage the most up-to-date data available at the time of publication.