Improving the Customer Experience, Boosting Productivity and Efficiency, and Reducing Costs
In 2017, shared services conferences buzzed with anticipation as banners proclaimed, “The robots are coming!” with robotic process automation (RPA) and chatbot technologies creating a wave of excitement soon followed by conversational agents, blockchain, and artificial intelligence (AI) promises. Though these technologies have created value in particular parts of our shared services processes, none have yet to revolutionize how we work. While some shared services organizations have successfully embraced RPA, particularly in finance, they have encountered challenges in scaling conversational AI, virtual agents, and chatbots across various processes due to the complexities and time-consuming nature involved in establishing governance and designing and implementing these solutions.
Fast forward to now, and we can confidently proclaim, “The robots are here!” The advancement of AI technologies, including generative AI, has paved the way for organizations to deliver greater value at an accelerated pace. Unlike the aforementioned technologies, which are focused on recognizing patterns given a distinct set of data, generative AI is capable of creating new content through a vast set of unstructured data that continues to grow as people use generative AI every day. By harnessing its capabilities, shared services organizations can increase productivity by more easily automating routine tasks and empowering their staff and customers to resolve issues more quickly and effectively.
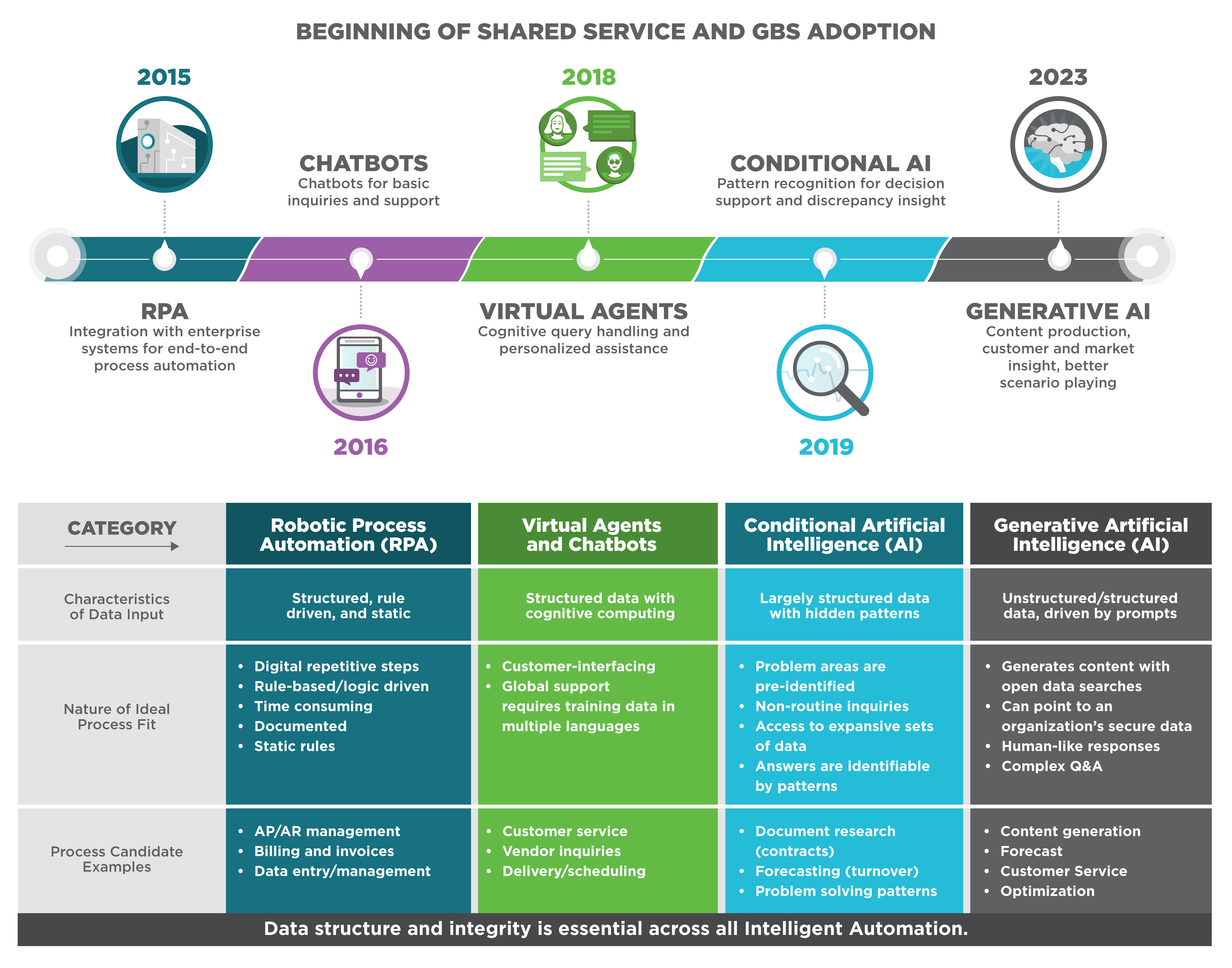
Many service centers are just beginning to explore generative AI to elevate the customer experience, drive productivity and efficiency, improve controls to enhance compliance, and optimize location strategies.
Elevate the Customer Experience
Leveraging cutting-edge generative AI algorithms can elevate the customer experience by providing personalized responses tailored to each customer’s role, region, and language, enabling virtual agents to provide more customer support with less manual training. As generative AI solutions are directly connected with traditional knowledge management systems, customers will be able to find answers faster (e.g., generative AI can search for a specific, contextual answer versus providing a list of knowledge articles that may be relevant for the user to research). By directly connecting generative AI solutions with internal, proprietary knowledge management solutions, organizations will be able to reduce the risk of sharing intellectual property with the rest of the world since their knowledge base won’t be included in the overall global generative AI data model.
With this technology, organizations can generate more human-like AI responses by leveraging human-sounding speech and continuous customer sentiment analysis, adapting the AI’s reactions to customer needs. Customers can be seamlessly transferred to Tier 1 and Tier 2 agents when generative AI cannot support the customer, and the AI can provide contextual information to the human agent for a seamless customer experience.
Generative AI may continue to play a role after customers are transferred to human agents. Envision equipping agents with tools that would enable a mid-conversation prompt, “How should I respond?” and immediately receiving an exceptional answer based on masses of valid internal (or external) data. But wait… there’s more. Large language modules can also translate native languages to Tier 1 and Tier 2 agents’ languages in near real-time speed. Barriers that have forced organizations to locate service centers in various parts of the world, primarily for language capability, are quickly being dismantled.
Drive Productivity and Efficiency
As generative AI becomes increasingly robust, businesses will be able to achieve a logarithmic increase in productivity and efficiency. It can automatically learn and streamline processes (within the organization’s parameters and rules), substantially reducing the cost of improving processes, enabling organizations to realize value much faster, and freeing up time and resources for more strategic objectives. Tier 1 and Tier 2 agents can be empowered with generative AI assistance (AI “co-pilot”), generating potential solutions or troubleshooting steps based on customer problem descriptions. Generative AI leapfrogs its AI predecessors with the ability to manage process discrepancies that historically stopped a robot in its tracks. It can realize, “I’m missing this information,” and go get it. Resolution of process “jams” may be converted from days or even weeks to just seconds.
Improve Controls to Enhance Compliance
Generative AI can be used to ensure rule-based protocol compliance, minimizing human error and driving higher compliance standards. The data available to generative AI includes SoX compliance guidelines, process-leading practices, tax regulations from multiple countries, and country/state/county regulations that may impact processes.
Be warned that the software can produce wrong answers; not all responses come with a data source. However, generative AI can act as an assistant to pressure test controls and compliance questions within shared services processes.
Optimize Location Strategies to Enhance Service and Reduce Costs
As we continue through uncertain economic times, many organizations are relooking at their location strategies and delivery models to gain immediate savings and scale by rethinking their delivery center locations. Location analysis has traditionally entailed laborious research on country/city socio-economic data, labor costs, turnover rates, infrastructure, and several other criteria. Generative AI gives us much quicker access to this data and the ability to run scenarios that optimize existing or new, low-cost locations. Additionally, augmenting workers already in lower-cost centers with AI “co-pilots” (i.e., AI-assisted support) empowers them to handle more complex work effectively. This strategic approach not only leads to significant cost reductions, but it also ensures that service quality is maintained and customer demands are met.
Examples of Process-Based Benefits
Here are several examples of how these benefits can translate into process-based work within a shared services center (along with expanding the scope of work service centers can provide):
- Customer Services (Tier 1)
- Augmented Tier 0 Support: Replace portions of Tiers 1 and 2 with Tier 0 in multiple languages or time zones. Enable Tier 0 to provide answers to frequently asked questions, provide guidance on basic- to medium-complexity inquiries, and assist with routine tasks, such as benefits enrollment or time and expense submission
- Sentiment Analysis: Automatically redirect agitated customers to experienced employees
- Finance (Tier 2)
- Accounts Receivable (AR): Optimize AR by short-listing customers most likely to pay (improved credit analysis
- Document Recognition: Utilize intelligent document recognition to automate document sorting and extraction processes
- Expense Management and Control: Automate expense management processes by analyzing and categorizing expenses, detecting policy violations, and flagging potential issues, which can provide real-time insights into spending patterns to help organizations control costs and improve expense management practices
- Loading historical financial reports and improving forecasting, planning, and budgeting with situational queries that test different scenarios
- Human Resources (Tier 2)
- Candidate Screening: Identify top candidates in screening based on criteria determined to drive high performance within the organization
- Employee Onboarding: Create personalized onboarding plans for new employees by generating tailored training materials, resources, and documentation based on their roles and responsibilities
- Performance Evaluation and Feedback: Analyze employee performance data, feedback, and key performance indicators to generate insights and recommendations for performance evaluations to assist managers in providing objective and constructive feedback
- Supply Chain and Procurement (Tier 2)
- Supply Chain Planning: Conduct end-to-end supply chain planning for advance out-of-stock prevention
- Supplier Discovery: Analyze a vast amount of supplier data, including supplier profiles, certifications, performance metrics, and user reviews, to generate a list of potential suppliers that align with specific procurement requirements
- Contract Analysis and Management: Analyze contracts, extracting key terms, conditions, and obligations, to identify inconsistencies, risks, or non-compliance issues
Importance of Continuous Improvement and Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
To unlock the full potential of generative AI, continuous improvement is essential. Shared services organizations must proactively update and retrain the model with new data and customer interactions to foster enhanced accuracy and performance. This iterative process enables the model to learn from real-world experiences, effectively managing an expanding range of inquiries.
It is crucial to exercise caution during the implementation of generative AI. It is largely unregulated and requires that organizations develop reasonable guardrails around how they use the technology. Many of its tools rely on retraining their databases using the questions and answers provided. To protect sensitive company data, it is advisable to establish a “wall” around the data through direct interfaces, preventing data from being shared with external databases. It is also vital to inform users that they are engaging with AI and not interacting with a human agent. Transparent communication fosters trust and helps manage user expectations effectively. Finally, periodic reviews of the system should be conducted to ensure its effectiveness. It is crucial to have human agents available to address complex or specialized issues that may arise and cannot be adequately resolved through self-service options.
Take the Next Step
By approaching generative AI implementation with some early exploration of use cases, shared services organizations can better understand where the tool will add the most value and begin to understand and effectively address the inherent challenges. This will give organizations a leap-start to developing faster analyses, better forecasts, and exceptional customer service.
Contact us to discuss how you can take the next step to enhance the services provided by your shared services organization and improve the employee experience.