Modernization that Connects Strategy, Systems, and Staff
Figure 1 - Operating Model Transformation
Before and After
Siloed Engineering, Operations, and Maintenance
Paper-Based Processes
Reactive Maintenance
Cross-Functional Governance
Mobile AI-Enabled Workforce
Predictive Operations
Operating Model Transformation
Before and After
Siloed Engineering, Operations, and Maintenance
Cross-Functional Governance
Paper-Based Processes
Mobile AI-Enabled Workforce
Reactive Maintenance
Predictive Operations
We’ve analyzed opportunities across nuclear operations to identify where changes in technology, processes, and workforce deployment can reduce costs while maintaining safety. This research catalogued specific improvements, ranging from remote monitoring to automated maintenance planning, and quantified potential annual savings of $60 million at a typical dual-unit plant. [1] We’ve also developed structured approaches for assessing how ready plants are for transformation (Digital Modernization, NRC Cybersecurity Compliance, Fleet-Wide Transformation). These approaches evaluate current business conditions, workforce challenges, and equipment obsolescence then compare existing initiatives against proven practices. The result is customized roadmaps that balance quick wins with strategic initiatives based on each plant’s specific situation.[2]
Finally, we’ve created rigorous methods for building modernization business cases that capture both immediate returns and long-term strategic value. At Vistra’s Comanche Peak, we developed a business case, demonstrating NPV of $74 million over 30 years (increasing to $685 million over 50 years) for comprehensive I&C upgrades, with payback in under 18 years. Critical to these results was properly accounting for the true cost trajectory of maintaining obsolete systems. At Constellation’s Limerick plant, our analysis revealed that obsolete safety-related I&C equipment costs escalate by more than 20% annually—far exceeding standard inflation assumptions of 3% to 5%.[3] This finding fundamentally changes modernization economics—what appears marginal under traditional assumptions becomes compelling when true obsolescence costs are recognized.
Implementation Insights: Four Keys to a Successful ION Operating Model
Through numerous ION implementations, consistent patterns have emerged that separate successful transformations from failed initiatives:
- Lead with Operating Model Design, Not Technology. The most successful efforts solve specific operational problems rather than deploy technology for its own sake. Digital tools deliver value only when embedded in redesigned work processes, redefined roles, and new decision-making structures. Technology enables transformation but doesn’t drive it.
- Build Scalable Fleet Governance. Programs with cross-functional oversight and clear standards move faster and deliver better results than on a plant-by-plant basis. Without enterprise governance protocols for investment decisions and implementation standards, modernization becomes an inconsistent patchwork that fails to capture fleetwide benefits.
- Design in NRC Cybersecurity and Compliance. As NRC’s Cybersecurity Rule enforcement intensifies, security architecture must be built into modernization from the outset, avoiding the need for retrofitting. This includes critical digital asset classification and hybrid OT-IT readiness. Retrofitting security after implementation creates delays, cost overruns, and compliance risks.
Ground Business Case Development in Operating Reality. Executives and regulators demand proven value, not projections. Successful business cases use actual plant data on labor costs, maintenance expenses, and obsolescence trends. Early wins with measurable results build momentum and unlock further investment.
Comprehensive Support for Nuclear Modernization: Strategy Through Execution
We understand how to align modernization efforts with licensing requirements, cost recovery pathways, and internal investment governance. Our ability to connect strategy, engineering, IT, and regulatory realities ensures that modernization can move from roadmap to reality.
Figure 2 illustrates ScottMadden’s ION Operating Model Pathway, progressing from initial assessment through fleetwide implementation. This structured approach ensures that each phase builds on the previous one, creating momentum and reducing implementation risk.
Figure 2 - ION Modernization Value Pathway

PHASE 1
Modernization Assessment & Planning

PHASE 2
Business Case
& Regulatory
Support

PHASE 3
Implementation
& Change Management

PHASE 4
Fleet-Wide
Scaling/ION Implementation
Figure 2 - ION Modernization Value Pathway

PHASE 1
Modernization
Assessment
& Planning

PHASE 2
Business Case
& Regulatory
Support

PHASE 3
Implementation
& Change
Management

PHASE 4
Fleet-Wide
Scaling/ION
Implementation
Our Integrated Service Offerings
ScottMadden delivers ION transformation through six integrated focus areas that address every aspect of modernization. As shown in Figure 3, our technical insight, operational discipline, and enterprise change leadership work together to create comprehensive transformation solutions.
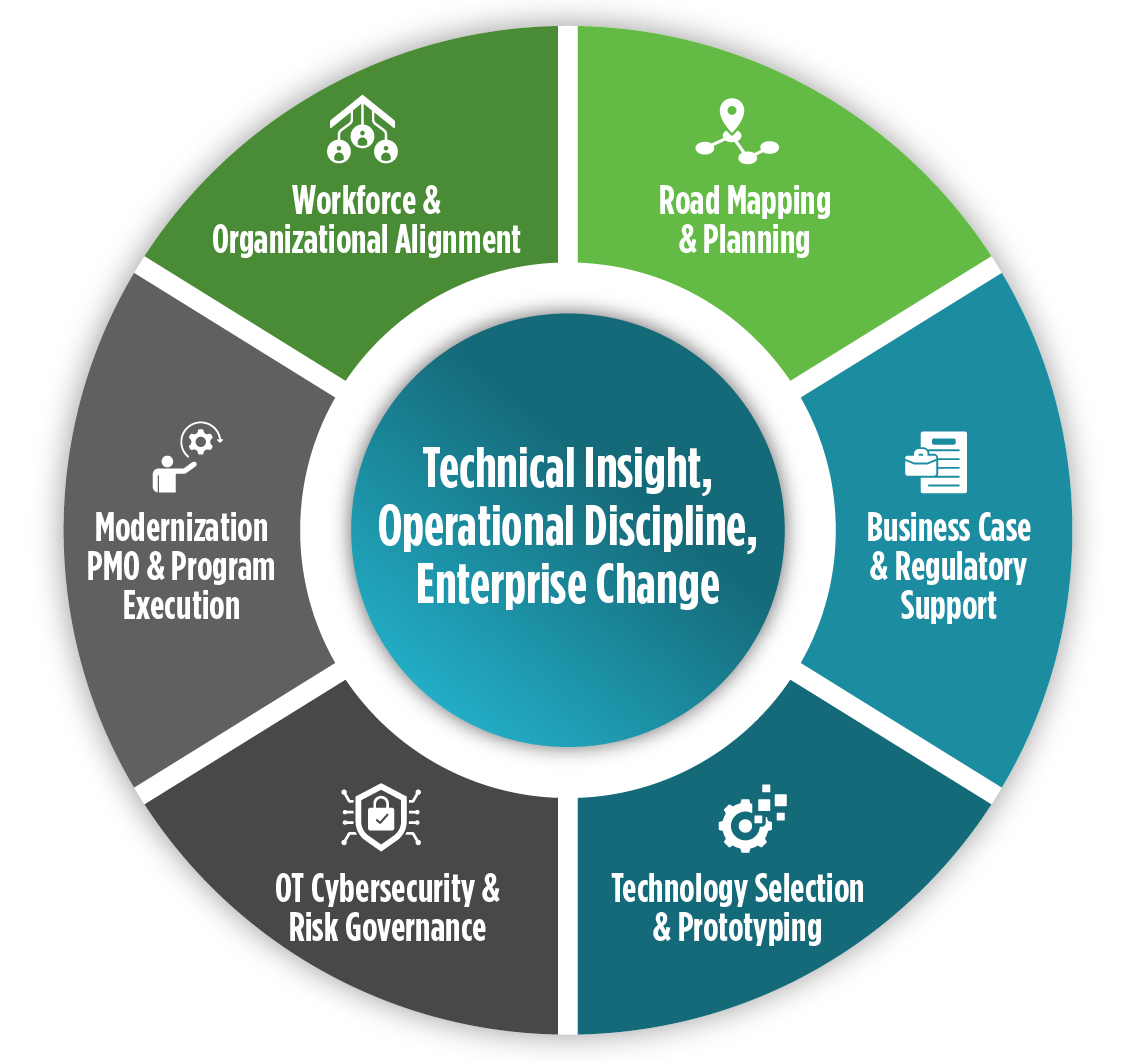

1. Road Mapping & Planning
- Plant modernization, innovation, and long-term operations planning
- Strategic modernization assessments tailored to site or fleet maturity
- Implementation of ION operating models
2. Business Case & Regulatory Support
- Capital planning and investment scenario modeling
- Cost-benefit analysis for digital infrastructure, I&C control system upgrades, and predictive maintenance technologies
- Regulatory strategy and rate case approach, licensing support, and integration with digital modernization filings
3. Technology Selection and Prototyping
- AI and machine learning use case development and pilot design
- Digital I&C control system upgrade planning and vendor coordination
- Advanced maintenance tools (e.g., condition-based maintenance, digital twins, drones, robotics) evaluation for operational fit
4. OT Cybersecurity & Risk Governance
- Secure data infrastructure planning for hybrid operations
- NRC Cybersecurity Compliance assessments and critical digital asset classification
- Cybersecurity architecture design and owner’s engineer support for digital systems
5. Modernization PMO & Program Execution
- Full life cycle program management for modernization rollouts
- Work management functional integration and process transformation
- Change enablement, communication planning, and stakeholder alignment
6. Workforce & Organizational Alignment
- NXT GEN® training, workforce strategy, and digital training program design
- Organizational redesign for integrated operations, human-system interface optimization, and mobile workforce enablement
The future of nuclear power requires comprehensive transformation, not isolated upgrades. Success demands an integrated approach that aligns operations, digital strategy, and organizational capabilities at fleet scale.
ScottMadden stands ready to guide your ION transformation journey. Contact us to discuss how we can help your organization achieve the operational excellence that ION enables.
Alex Tylecote also contributed to this article.
[1] Remer, J., Thomas, K., Martin, L., & Lawrie, S. (2021). Process for Significant Nuclear Work Function Innovation Based on Integrated Operations Concepts (No. INL/EXT-21-64134). Idaho National Laboratory (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States).
[2] Remer, S. J., Martin, L., et al. (2023). Applying the ION Business Model to a Domestic Nuclear Plant: Assessment and Transformation Implementation Plan (No. INL/RPT-23-73942). Idaho National Laboratory (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States).
[3] Hunton, P. J., Sr., & England, R. T. (2020). Safety-Related Instrumentation & Control Pilot Upgrade Initial Scoping Phase Implementation Report and Lessons Learned (No. INL/EXT-20-59809). Idaho National Laboratory (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States).





